You’ve made it to page one of Google. But are you actually getting clicks?
If you’re like most website owners, you’ve invested countless hours into SEO, only to find that ranking on the first page doesn’t guarantee traffic. Here’s the reality: the top three results on Google capture 54.4% of all clicks, while position ten gets just 2.4%. That’s where search engine positioning comes in.
Search engine positioning SEO is the strategic practice of optimizing specific pages on your website to achieve higher rankings for target keywords. Unlike broad SEO strategies that focus on your entire website, positioning zeros in on individual pages to maximize their visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover seven proven strategies to improve your search engine positioning, understand how it differs from traditional SEO, and learn how to adapt your approach for AI-powered search in 2025.
What Is Search Engine Positioning?
Search engine positioning is the practice of optimizing specific pages on your website to achieve higher rankings in search engine results pages. While SEO encompasses your entire digital presence, search engine positioning focuses on improving the visibility of individual pages for their target keywords.
Think of it this way: SEO is the umbrella strategy, and search engine positioning is one of the most targeted tools underneath it. When you optimize a specific blog post, product page, or service page to rank higher for particular search queries, you’re practicing search engine positioning. For a deeper understanding of how all SEO elements work together, check out our comprehensive SEO chart guide.
According to research by Backlinko, moving up just one position in search results can improve your click-through rate by up to 30%. That single position change could mean the difference between steady organic traffic and watching potential customers click on your competitors instead.
Modern search engine positioning also extends beyond traditional organic results. Today, you need to consider SERP features like featured snippets, People Also Ask boxes, video results, and increasingly, AI Overviews. Each of these represents an opportunity to capture visibility and clicks.
Search Engine Positioning vs. SEO: What’s the Difference?
While these terms are often used interchangeably, understanding their differences is crucial for developing an effective digital marketing strategy. If you’re working with an SEO strategist, they’ll typically focus on both aspects as part of a comprehensive approach.
Main Focus
Search engine optimization (SEO) is a comprehensive, website-wide strategy. It encompasses technical SEO (site speed, crawlability, mobile optimization), keyword research, content strategy, link building, and user experience improvements across your entire domain.
Search engine positioning, on the other hand, narrows the focus to specific pages and keywords. It’s about taking individual pages and optimizing them to rank as high as possible for their target search queries.
For example, if you run an athleisure retailer, your SEO strategy might involve developing various types of content, improving site architecture, and building domain authority. Your search engine positioning efforts would focus on getting a specific product collection page to rank in the top three for “women’s workout shorts.”
Timeline
SEO is a long-term investment. Google themselves acknowledge that comprehensive SEO strategies can take four months to a year to show significant results. You’re building authority, trust, and topical relevance over time.
Search engine positioning can deliver faster results. Because you’re working with pages that are already indexed and potentially ranking, optimizations can be reflected in days to weeks.
Quick Comparison
| Aspect | SEO | Search Engine Positioning |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Entire website | Specific pages |
| Focus | Technical SEO, content, links, UX | Ranking improvement for target keywords |
| Timeline | 4-12 months for full results | Days to weeks for indexed pages |
| Goal | Overall site visibility & authority | Top positions for specific queries |
Why Search Engine Positioning Matters in 2025
The search landscape has fundamentally changed, making strategic positioning more important than ever.
The Click-Through Rate Reality
The data on click-through rates paints a clear picture of why position matters. According to First Page Sage’s CTR research:
27.6%
Position #1 CTR
54.4%
Top 3 Combined
2.4%
Position #10 CTR
+30%
CTR per Position Up
These numbers reveal a stark reality: if you’re not in the top three positions, you’re missing out on the majority of organic traffic for your target keywords.
The AI Overview Factor (NEW for 2025)
AI has transformed how people discover information online. More than 50% of Google queries now trigger AI Overviews, which means the traditional “ten blue links” are no longer the only game in town.
Being cited in AI-generated answers represents a new form of positioning. Even if you don’t hold the top organic position, getting your content referenced in AI Overviews can drive significant visibility and traffic. Zero-click searches are increasing, making it essential to think beyond traditional rankings to overall SERP presence.
Business Benefits
Effective search engine positioning delivers tangible business outcomes:
- More organic traffic without increasing ad spend
- Better brand visibility and trust
- Competitive advantage by outranking competitors
- Higher conversions from qualified organic traffic
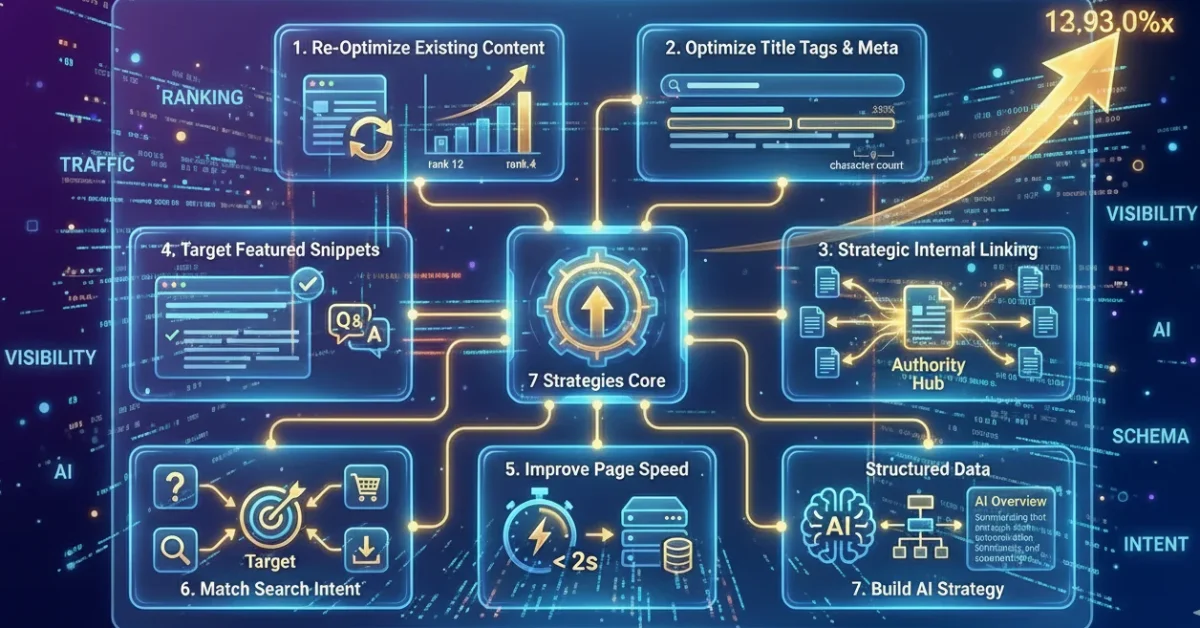
7 Proven Strategies to Improve Your Search Engine Positioning
Now let’s dive into actionable strategies you can implement to improve your rankings and maximize your SERP visibility.
1. Re-Optimize Your Existing Content
Your first priority should be pages already ranking on page one or two of Google. Why? Because Google already considers these pages relevant for your target keywords.
Start with Google Search Console. Navigate to the Performance section and sort queries by position. Look for keywords where you’re ranking between positions 8-20—these are your “striking distance” opportunities.
- Update outdated information, statistics, and examples
- Expand content depth to cover missing subtopics
- Improve readability with better formatting and structure
- Add relevant secondary keywords and semantic terms
2. Optimize Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Your title tag and meta description are your first opportunity to capture clicks. They’re what users see in search results before deciding whether to visit your page.
For title tags: Keep them under 60 characters. Place your primary keyword near the front. Use power words like “Ultimate,” “Proven,” “Complete,” or “Guide.” For guidance on creating effective service pages, see our local SEO landing page examples.
For meta descriptions: Aim for 150-160 characters. Include your target keyword naturally. Add a clear call-to-action that tells users what they’ll gain.
3. Use Strategic Internal Linking
Internal links help Google understand how your content is related and pass authority from high-performing pages to ones you want to rank higher.
- Link from high-authority pages to pages you want to boost
- Use keyword-rich anchor text instead of “click here”
- Create topic clusters that establish topical authority
- Fix broken links regularly to maintain link equity
4. Target Featured Snippets and SERP Features
Featured snippets appear at the very top of search results, above position one. Capturing a featured snippet can dramatically increase your visibility and traffic.
- Identify keywords that currently trigger featured snippets
- Format content to match the snippet type (paragraph, list, table)
- Answer questions directly in 40-60 words
- Use clear headings that match common question formats
- Implement schema markup for rich results
5. Improve Page Speed and Core Web Vitals
Page speed and Core Web Vitals directly impact both your rankings and user experience. Target a page load time under 2 seconds.
- Optimize images: Compress files and use WebP format
- Minimize HTTP requests: Reduce scripts and stylesheets
- Enable browser caching: Store static resources locally
- Use a CDN: Distribute content globally for faster delivery
Use Google PageSpeed Insights and the Core Web Vitals report in Search Console to identify specific issues.
6. Match Search Intent Precisely
Search intent is the reason behind a user’s query. Google prioritizes content that best satisfies what users are actually looking for.
The four main types of search intent are:
- Informational: Users want to learn something
- Navigational: Users want to find a specific page
- Commercial: Users are researching before buying
- Transactional: Users are ready to take action
Analyze the top 10 results for your target keyword to understand what Google wants, then create content that meets or exceeds what’s already ranking. For local businesses, understanding how the Google Local Pack works is equally important.
7. Build a Search Engine Positioning Strategy for AI
With AI Overviews becoming increasingly prominent, your positioning strategy must evolve. Being cited in AI-generated answers is becoming as valuable as traditional rankings.
- Structure content for AI parsing: Use clear headings and concise paragraphs
- Implement comprehensive schema markup: Help AI understand your content
- Focus on E-E-A-T signals: Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust
- Provide direct, concise answers: Aim for 40-60 words for key definitions
How to Measure Search Engine Positioning
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Tracking your positioning helps you understand what’s working and where to focus your efforts.
Using Google Search Console
Google Search Console is your primary free tool for monitoring positioning:
- Navigate to Performance → Search Results to see your data
- Track average position, clicks, impressions, and CTR for each query
- Filter by page to see positioning for specific URLs
- Use the URL Inspection tool to request re-indexing after optimizations
Position Tracking Tools
For more comprehensive tracking, consider dedicated position tracking tools:
- Semrush Position Tracking: Monitors rankings daily and compares you against competitors
- Ahrefs Rank Tracker: Tracks positions across multiple search engines and locations
- SE Ranking: Offers detailed SERP feature tracking and competitor analysis
For local businesses, don’t forget to use our Google Review Calculator to understand how reviews impact your local positioning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between SEO and search engine positioning?
SEO is a comprehensive, website-wide strategy that encompasses technical optimization, content strategy, link building, and more. Search engine positioning is a subset of SEO that focuses specifically on improving rankings for individual pages and their target keywords. Think of SEO as the overall game plan and positioning as the tactical plays for specific content.
How long does it take to improve search engine positioning?
Changes to already-indexed pages can be reflected in search results within days to weeks. However, significant ranking improvements typically take 2-4 weeks to materialize. You can speed up the process by using Google Search Console to request re-indexing after making optimizations.
What is a good search engine position?
The top three positions capture 54.4% of all clicks, with position one receiving approximately 27.6% CTR. Ideally, you want your most important pages ranking in the top three. However, appearing anywhere on page one is valuable, and positions 4-10 still receive meaningful traffic.
Can you improve positioning without backlinks?
Yes, you can improve positioning through content optimization, internal linking, improving user experience, and optimizing for search intent. However, backlinks remain one of Google’s strongest ranking signals. For competitive keywords, a combination of on-page optimization and quality backlink acquisition typically produces the best results.
Does search engine positioning matter for AI search?
Absolutely. In 2025, search engine positioning extends beyond traditional rankings to include citations in AI Overviews. With more than 50% of Google queries triggering AI-generated summaries, getting your content cited in these answers is becoming increasingly important.